Types of entities in ARC+
Home > 01 Getting Started > Types of entities in ARC+
Types of entities in ARC+
The basic unit that the system identifies is a geometric entity or element. To enhance the designing process, the system provides various entities, each having its own characteristics and function. This paragraph talks about following entities in brief. For detailed description, refer to the corresponding chapters of the manual:
Wireframe (lines and arcs)
Polygons (surface and symbol)
Solid bodies (simple and complex)
Walls
Staircases
Hatches, patterns and linear patterns
Points
Help Lines
Placed Objects
Images (raster data)
Texts
Dimensions
Wire Entities
A wireframe entity (line or arc) is a graphic entity composed of 2D lines and devoid of surface or solid properties. It cannot be expanded to create a solid entity. A line can be defined between any two points in three dimensions; circles or arcs can be defined on any plane. A 3D construction of wire entities is not regarded as a solid entity and its hidden lines cannot be removed (i.e., it remains transparent). Each segment remains a separate entity.
Wire entities may be used for such things as graphic additions to the surface of solid entities, site boundaries, roads, etc., and also for finalizing 2D drawings. They may also be used in the solid model to represent, for example, glazing mullions of an atrium where a transparent effect is required. A loop of wire entities may be converted into a polygon.
Polygons
Polygons are 2D series of lines and arcs that possess 3D qualities. They may be expanded into 3D solids by a variety of means. All parts of a polygon should lie on the same plane in order to avoid problems when creating solid entities. Negative solids—which are actually holes—can be created for openings in polygons and walls.
The basic polygon creation commands create polygons that are sequences of lines. When a polygon is closed it becomes a surface polygon that behaves as an opaque surface in the solid viewing mode. You also have the option to convert this to a transparent symbol polygon. A polygon may be exploded into a series of wire entities with the loss of all 3D properties.
Solid Body — Simple
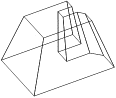
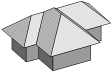
A solid entity is a 3D entity comprised of two polygons joined at their vertices by connecting edges. There are various methods for creating solid entities, e.g., expanding a polygon to create a prism, or connecting two polygons to create a two-base entity. Solid entities can be either positive (e.g., columns) or negative (e.g., openings in walls). They can be displayed in the following display modes:
Wire frame (transparent)
Hidden lines removed
Colored surfaces
Colored shaded surfaces
Monochromatic shaded surfaces
Colored surfaces and shadows
monochromatic surfaces and shadows
NOTE The colored surfaces can not be printed or plotted.
Solid Body - Complex
Complex solids are special types of solids. They are created in a variety of ways:
Rotating a polygon to form a rotational solid
The result of a set operations process
Remaining part of a wall or solid entity after sectioning
They no longer bear the characteristics of the original entity type. All the faces of the solid are surface polygons.
Wall Entities
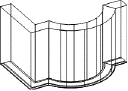
Wall entities are 2D and 3D entities with special properties, such as multi-layers and height attributes. Walls (and) openings are stored in the ARC+ libraries. You control the positions of walls using symmetry and alignment. Multi-layer wall junctions formed by intersecting walls are resolved by system generated solutions.
Initially created in 2D, you expand the walls into 3D whenever desired. Openings, such as doors and windows may be inserted into the wall in 2D as a symbol containing all 3D attributes or in 3D as a void. The system also provides solutions called end conditions, where openings have to be integrated with the multi-layer walls.
Stairs
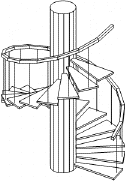
Stairs are either 2D or 3D entities that are generated automatically by ARC+, after defining a series of parameters. Since a number of parameters are interdependent, you decide which parameters are fixed and which are to be calculated by the system. In addition you can also define the ranges for the parameters.
Placed Objects
Objects are 2D or 3D models stored in a directory that are placed within another file. These entities behave as single entities irrespective of their composition in the original file. A placed object is actually a reference to the external model. Hence, if that model is changed, all instances of the placed objects in other models are automatically updated. You may arrange placed objects in a hierarchy of up to five levels.
Images
Images from digital camera, scans or render programs, so called raster files are fully supported. Once they are placed from external file formats they are fully embedded in ther ARC+ file format. This enables you to control, clip, edit, scale and filter them with a huge variaty of filters. This will remove or lower your need of external raster editing software. The images can be imported and exported via 46 formats. Images including alpha-channel can be displayed with transparent areas. There is control to show images in front or back but also to cover vector data or not.
There are on top of the standard functionality two ADD ONS using the raster image support.
ARC+ SKETCH is a an ADDON license giving both a menu and a huge collection (thousands) of sketched materials and objects. It enables you to work on scale and render in 2D with a hand drawn look in a minimum of time and effort
ARC+ Photo is an ADDON license enabling you to rectify photo images from products, buildings or materials.
For more info we refer to chapter 27
Hatches, Area Fill Patterns & Linear Patterns
The hatch entities are fill patterns for polygons. Hatching is created by defining parameters for a series of parallel lines drawn in specified directions. A closed polygon is necessary for delineating the hatch border, but may be subsequently removed. The polygon can be hatched on any plane in three dimensions.
The area fill patterns are based on a planar motif or design, repeated as necessary to fill a polygon-surrounded area. linear patterns are predesigned units repeated along an invisible line. These patterns are formed from text character entities and exhibit text attribute properties. ARC+ contains libraries with predefined patterns, to which of course, you can add your own.
Help Lines
Help lines are guide lines to aid the construction of other entities or to locate points in space. Usually used in a temporary manner, help lines are easily inserted and removed. Help lines are dotted to differentiate them from other lines. They can be created in any plane in three dimensions. Help lines cannot be plotted or printed, or transferred to the DXF format.
Text and Dimensions
The text entities are the alphanumeric data that can be added to your model. Text can be created and viewed in any of the major planes. You can control different aspects of text, such as the font, spacing, justification and the relative size when placing or plotting.
Dimension lines are comprised of a line, line extension marks (tick marks) and the associated "text"—the dimension value itself. ARC+ automatically provides precision measurements of the real dimensions of your model. The attributes of text and dimension lines are similar.
Points
The points are special entities that are you can use to mark locations in space. They consist of three intersecting lines, each parallel to one of the major axes. When snapping to a point the cursor is always attracted to the precise intersection of the lines rather than their ends. The points can be deleted using a special command. They exist in the database and can be plotted. They can be selected separately using a special selection options. Points must not be confused with help points (which are help line entities) or with markers which do not exist in the database, are associated with arcs, placed objects or text entities and are deleted when the parent entity is deleted.