Projecting a Polygon to a New Plane
Home > 04 Polygons and Solids > Projecting a Polygon to a New Plane
Projecting a Polygon to a New Plane
Project or copy and project an existing polygon onto a new plane.
\proj
When you move a polygon, its dimension remains unchanged. When you project a polygon, however, the original entity becomes distorted if the new plane is not parallel to the original one. For example, if you require a polygon on a pitched roof, you can create it on the floor (xy plane) and project it onto the roof plane. The dimension of the polygon in the direction of the slope of the roof will be elongated.
Operation
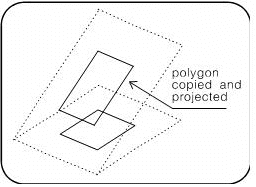
State whether you wish to project the polygon itself to the new plane or project a copy of it while leaving the original in position.
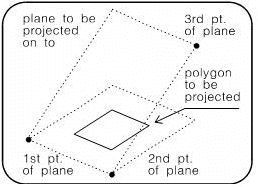
Specify along which of the major axes, x, y or z, you wish to project. Define the plane onto which the polygon is to be projected by defining three points.
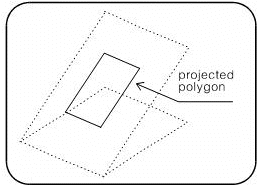
Indicate the polygon to be projected.
State whether you wish to keep the result. If you reject the result, the original state is restored.
 NOTE If you projected a polygon (without copying) that is part of a simple solid, the resulting solid is modified accordingly (shortened or lengthened).
NOTE If you projected a polygon (without copying) that is part of a simple solid, the resulting solid is modified accordingly (shortened or lengthened).
Polygons that are part of a complex solid are copied and projected. They cannot be projected only.
Two-dimensional polygons containing arcs are projected, while each of the arcs is changed to seven line segments. The command may not be executed on a polygon of a simple prism (solid) that includes an arc.
Two-dimensional walls cannot be projected. Polygons that are part of openings can be projected along the z axis only.